Wisconsin state tax plays a crucial role in funding public services and infrastructure within the state. From education to healthcare, these taxes ensure that residents receive essential services. Whether you're a resident, business owner, or simply curious about how taxes work in Wisconsin, this guide will provide you with all the necessary information.
Taxes are an integral part of any economy, and understanding how they function is essential for both individuals and businesses. In Wisconsin, the state tax system is designed to be fair and efficient, ensuring that revenue is collected to support vital programs and services.
This article will explore the intricacies of Wisconsin state tax, including income tax, sales tax, property tax, and other relevant tax obligations. By the end of this guide, you'll have a clear understanding of what WI state tax entails and how it impacts you.
Read also:Asian Actresses Hot
Table of Contents
- Introduction to WI State Tax
- WI Income Tax
- WI Sales Tax
- WI Property Tax
- Other Taxes in Wisconsin
- Tax Filing Process
- Tax Exemptions and Deductions
- WI State Tax Reforms
- Common Questions About WI State Tax
- Conclusion
Introduction to WI State Tax
Wisconsin state tax is a system designed to collect revenue from residents and businesses to fund public services. The state tax structure includes income tax, sales tax, property tax, and other levies. These taxes contribute to the state's budget, ensuring that essential services such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure are adequately funded.
Understanding WI state tax is crucial for residents and businesses alike. By familiarizing yourself with the tax obligations, you can ensure compliance and take advantage of available deductions and exemptions.
WI Income Tax
Overview of Wisconsin Income Tax
Wisconsin income tax is a progressive tax system with multiple brackets. The tax rates vary depending on the taxpayer's income level. As of the latest updates, the state income tax rates range from 4% to 7.65% for the highest earners.
Key points about WI income tax include:
- Progressive tax structure with multiple brackets.
- State income tax is calculated based on federal adjusted gross income (AGI).
- Residents and non-residents earning income in Wisconsin are subject to state income tax.
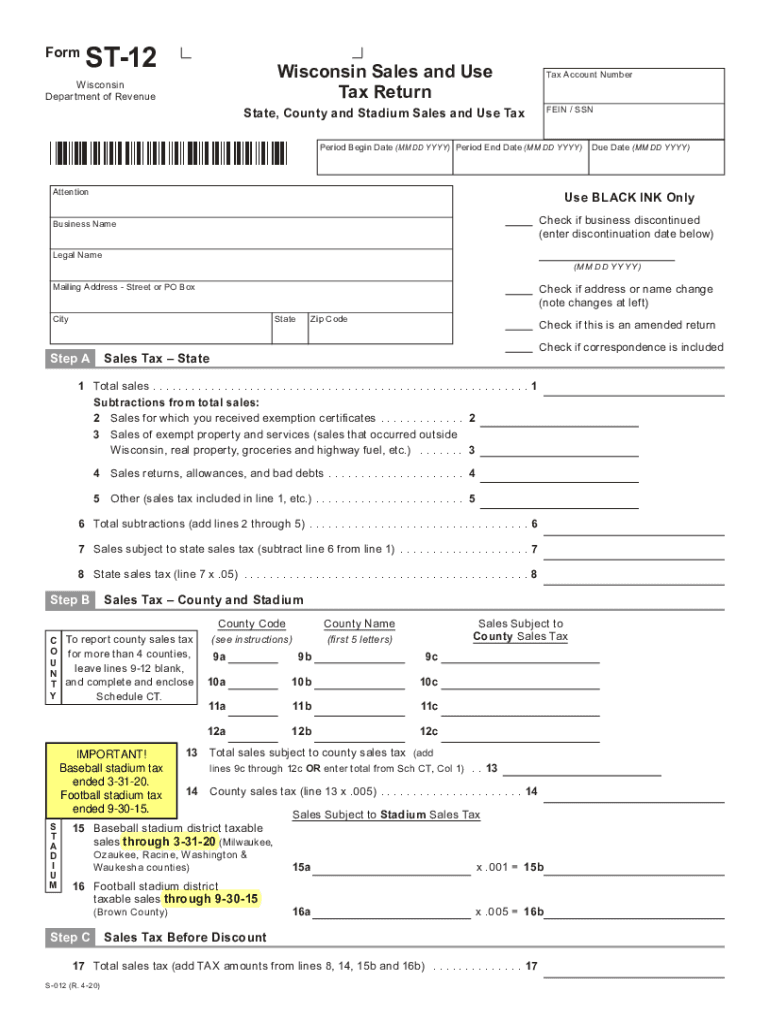
WI Sales Tax
Understanding Wisconsin Sales Tax
Wisconsin sales tax is a consumption tax levied on the sale of goods and services. The state sales tax rate is currently set at 5%, with additional local sales taxes that may apply depending on the location.
Important aspects of WI sales tax include:
Read also:Pining For Kim By Tailblazer An Indepth Exploration Of Love Desire And Creativity
- State sales tax rate of 5%.
- Local sales taxes can increase the total tax rate in certain areas.
- Certain items, such as groceries and prescription medications, are exempt from sales tax.
WI Property Tax
Wisconsin Property Tax Explained
Property tax in Wisconsin is a significant source of revenue for local governments. It is assessed based on the market value of real estate properties. Property tax rates vary across different municipalities, with some areas having higher rates than others.
Key features of WI property tax:
- Based on the assessed value of real estate properties.
- Local governments determine property tax rates.
- Property tax contributes to funding schools, public safety, and other local services.
Other Taxes in Wisconsin
Exploring Additional Taxes
In addition to income, sales, and property taxes, Wisconsin imposes other taxes that residents and businesses should be aware of. These include:
- Gasoline tax: A tax on fuel purchases to fund transportation infrastructure.
- Cigarette tax: A tax on tobacco products to discourage smoking and generate revenue.
- Excise tax: Applied to specific goods and services, such as alcohol and gambling.
Tax Filing Process
How to File Wisconsin State Taxes
Filing Wisconsin state taxes involves several steps, including gathering necessary documents, calculating your tax liability, and submitting your return. The Wisconsin Department of Revenue provides resources and tools to assist taxpayers in the filing process.
Tips for filing WI state taxes:
- Gather all relevant documents, such as W-2 forms and receipts for deductions.
- Use tax software or consult a tax professional for assistance.
- Submit your return by the deadline to avoid penalties.
Tax Exemptions and Deductions
Maximizing Your Tax Savings
Wisconsin offers various exemptions and deductions to help taxpayers reduce their tax liability. These include deductions for dependents, education expenses, and certain medical expenses.
Some common exemptions and deductions in Wisconsin:
- Homestead credit for homeowners.
- Educator expense deduction for teachers.
- Retirement income exclusion for seniors.
WI State Tax Reforms
Recent Developments in Wisconsin Taxation
Wisconsin has implemented several tax reforms in recent years to improve the state's tax system. These reforms aim to simplify the tax code, reduce burdens on taxpayers, and increase transparency.
Notable tax reforms in Wisconsin:
- Reduction in income tax rates for middle-income earners.
- Expansion of homestead credit for low-income homeowners.
- Introduction of new deductions for small businesses.
Common Questions About WI State Tax
Answers to Frequently Asked Questions
Many residents and businesses have questions about Wisconsin state tax. Here are answers to some common queries:
- Q: Who must file a Wisconsin state tax return? A: Residents, part-year residents, and non-residents earning income in Wisconsin must file a return.
- Q: What is the deadline for filing Wisconsin state taxes? A: The deadline is typically April 15th, but extensions can be requested if needed.
- Q: Are there penalties for late filing or payment? A: Yes, penalties and interest may apply for late filings or payments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding what is WI state tax is essential for ensuring compliance and maximizing tax savings. From income tax to property tax, each component of the state tax system plays a vital role in funding public services. By staying informed about tax obligations, exemptions, and reforms, you can make the most of your financial situation.
We encourage you to take action by reviewing your tax situation, consulting a tax professional if needed, and sharing this article with others who may benefit from the information. For more insights on Wisconsin state tax, explore our other articles on related topics.