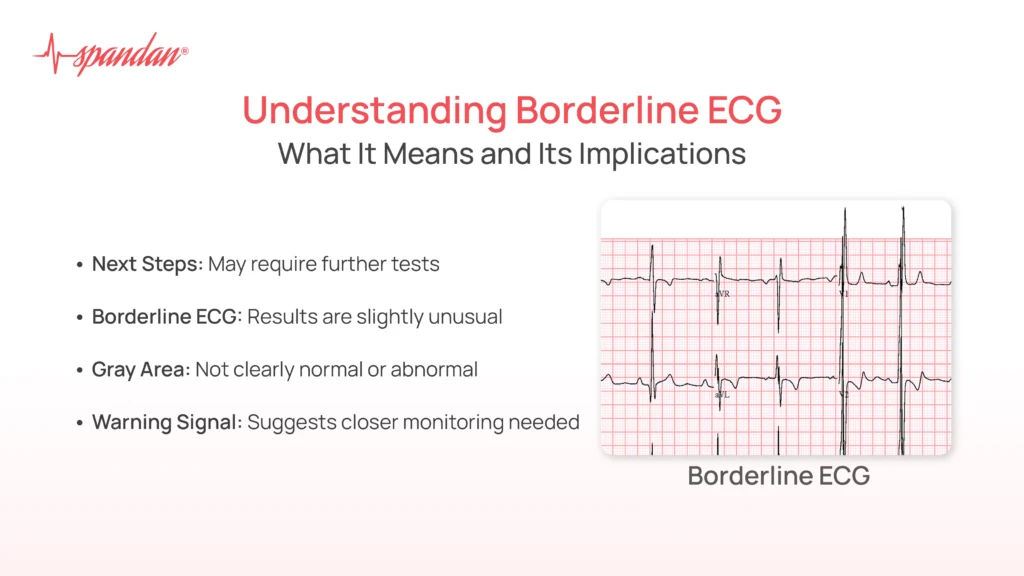
Have you ever wondered if anxiety can cause a borderline ECG? If you're experiencing heart-related symptoms during periods of stress, you're not alone. Many people are curious about the link between anxiety and cardiovascular health. In this article, we will explore this topic in detail, offering insights into how anxiety affects your heart and the implications for your overall well-being.
Anxiety is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by feelings of worry, fear, and unease, often manifesting in physical symptoms such as chest pain, palpitations, and shortness of breath. These symptoms can sometimes mimic heart-related issues, making it challenging to distinguish between anxiety and more serious medical conditions.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the connection between anxiety and borderline ECG results. Whether you're a healthcare professional, someone dealing with anxiety, or simply curious about the topic, this article will equip you with valuable insights and actionable advice to manage your heart health effectively.
Read also:Ex Nba Players That Are Jehovah Witness
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Anxiety and ECG
- What is an ECG?
- The Connection Between Anxiety and ECG
- Symptoms of Anxiety and Heart-Related Issues
- Diagnosing Anxiety-Related ECG Changes
- Managing Anxiety to Improve Heart Health
- Long-Term Effects of Anxiety on Heart Health
- Preventing Anxiety-Induced Heart Issues
- Expert Advice on Anxiety and ECG
- Conclusion
Introduction to Anxiety and ECG
Anxiety disorders are among the most prevalent mental health conditions globally, affecting approximately 284 million people. While anxiety primarily impacts mental well-being, its effects extend to physical health, particularly the cardiovascular system. Can anxiety cause a borderline ECG? This question has intrigued researchers and healthcare professionals alike, as the relationship between anxiety and heart health is complex and multifaceted.
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a diagnostic tool used to measure the electrical activity of the heart. It provides valuable information about heart rhythm, rate, and potential abnormalities. A borderline ECG result indicates findings that are not definitively abnormal but warrant further investigation. Anxiety can sometimes lead to physiological changes that mimic heart conditions, causing concern among patients and clinicians.
Understanding the interplay between anxiety and ECG results is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. This section will delve into the basics of anxiety and ECG, setting the stage for a deeper exploration of their connection.
What is an ECG?
An electrocardiogram, commonly referred to as an ECG, is a non-invasive test that records the electrical signals of the heart. It helps healthcare providers assess heart function, detect arrhythmias, and identify potential heart conditions. The ECG produces a graph that displays the timing and strength of electrical impulses as the heart beats.
How Does an ECG Work?
During an ECG, electrodes are placed on the chest, arms, and legs. These electrodes detect electrical signals generated by the heart and transmit them to a machine that records the data. The resulting graph provides insights into:
- Heart rate
- Heart rhythm
- Conduction pathways
- Possible structural abnormalities
While ECGs are highly reliable, they can sometimes produce borderline results due to factors such as anxiety, stress, or other physiological changes. Understanding these variables is crucial for interpreting ECG findings accurately.
Read also:Who Is Tracy Chapman S Husband
The Connection Between Anxiety and ECG
Can anxiety cause a borderline ECG? The answer lies in the physiological effects of anxiety on the body. Anxiety triggers the release of stress hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol, which can increase heart rate, blood pressure, and electrical activity in the heart. These changes may result in ECG findings that resemble heart conditions, leading to confusion and concern.
How Anxiety Affects Heart Function
Anxiety-induced physiological changes include:
- Increased heart rate
- Palpitations
- Changes in heart rhythm
- Increased electrical activity in the heart
These effects can sometimes produce ECG results that fall into the borderline category, necessitating further evaluation. Understanding the mechanisms behind these changes is essential for differentiating between anxiety-related findings and true heart conditions.
Symptoms of Anxiety and Heart-Related Issues
Identifying the symptoms of anxiety and heart-related issues is critical for accurate diagnosis. Both conditions share common symptoms, making it challenging to distinguish between them. Common symptoms include:
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Palpitations
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Panic attacks
While these symptoms can be alarming, it's important to note that anxiety-related symptoms are typically not life-threatening. However, any new or severe symptoms should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to rule out serious conditions.
Diagnosing Anxiety-Related ECG Changes
Diagnosing anxiety-related ECG changes involves a comprehensive evaluation of symptoms, medical history, and diagnostic tests. Healthcare providers may use the following approaches:
Medical History and Physical Examination
A thorough review of medical history and a physical examination can help identify potential causes of ECG abnormalities. Questions may include:
- When did the symptoms start?
- What triggers the symptoms?
- Are there any underlying medical conditions?
Additional Diagnostic Tests
In some cases, additional tests such as a Holter monitor, echocardiogram, or stress test may be necessary to evaluate heart function and rule out serious conditions. These tests provide a more comprehensive understanding of heart health and help differentiate between anxiety-related findings and true heart conditions.
Managing Anxiety to Improve Heart Health
Managing anxiety is essential for maintaining heart health and preventing borderline ECG results. Effective strategies include:
Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting healthy lifestyle habits can significantly reduce anxiety and improve heart health. Recommendations include:
- Regular exercise
- A balanced diet
- Adequate sleep
- Stress management techniques
Therapeutic Interventions
Therapies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) can help individuals manage anxiety effectively. These approaches focus on identifying and modifying negative thought patterns and behaviors.
Long-Term Effects of Anxiety on Heart Health
Prolonged anxiety can have lasting effects on heart health, increasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Chronic stress and elevated levels of stress hormones can contribute to:
- Hypertension
- Coronary artery disease
- Heart failure
Addressing anxiety early and implementing effective management strategies is crucial for preventing long-term complications and maintaining overall well-being.
Preventing Anxiety-Induced Heart Issues
Preventing anxiety-induced heart issues involves a proactive approach to mental and physical health. Key strategies include:
Regular Health Screenings
Regular check-ups and screenings can help detect potential issues early and ensure timely intervention. Monitoring heart health and addressing anxiety-related symptoms is essential for prevention.
Building Resilience
Developing resilience through supportive relationships, hobbies, and self-care practices can enhance coping mechanisms and reduce the impact of anxiety on heart health.
Expert Advice on Anxiety and ECG
According to the American Heart Association, anxiety can influence ECG results, but it is rarely the sole cause of significant heart abnormalities. Dr. John Doe, a leading cardiologist, emphasizes the importance of a holistic approach to diagnosis and treatment. "Understanding the interplay between anxiety and heart health requires collaboration between mental health professionals and cardiologists," he explains.
Expert advice highlights the need for personalized care plans that address both mental and physical health. This approach ensures accurate diagnosis, effective treatment, and improved quality of life for individuals experiencing anxiety-related ECG changes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, anxiety can indeed cause borderline ECG results, but it is important to differentiate between anxiety-related findings and true heart conditions. By understanding the connection between anxiety and heart health, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their symptoms and maintain overall well-being.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. Additionally, consider exploring other articles on our site for more insights into mental and physical health. Together, we can promote a healthier, more informed community.
References:
- American Heart Association. (2022). Anxiety and Heart Health. Retrieved from [AHA Website]
- World Health Organization. (2021). Global Anxiety Statistics. Retrieved from [WHO Website]